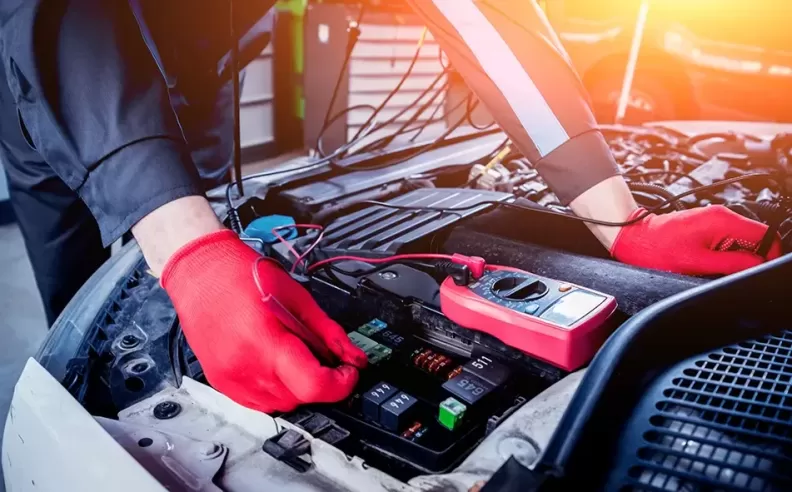
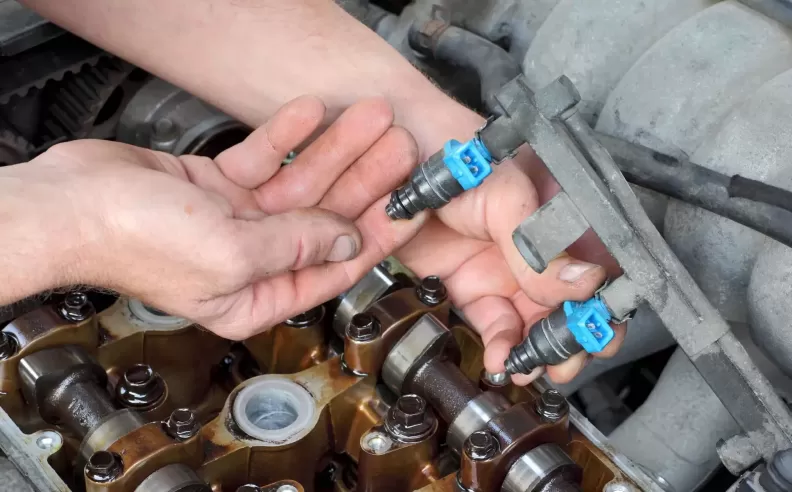
Modern vehicles heavily rely on complex electrical systems that power various components, ranging from ignition and lighting to entertainment and safety features. When these systems encounter problems, diagnosing and fixing car electrical issues can be challenging for many car owners. However, with a systematic approach and a basic understanding of the electrical components, you can successfully troubleshoot and resolve common car electrical problems without having to rely solely on professional help. This article will guide you through the process of diagnosing and fixing car electrical issues.
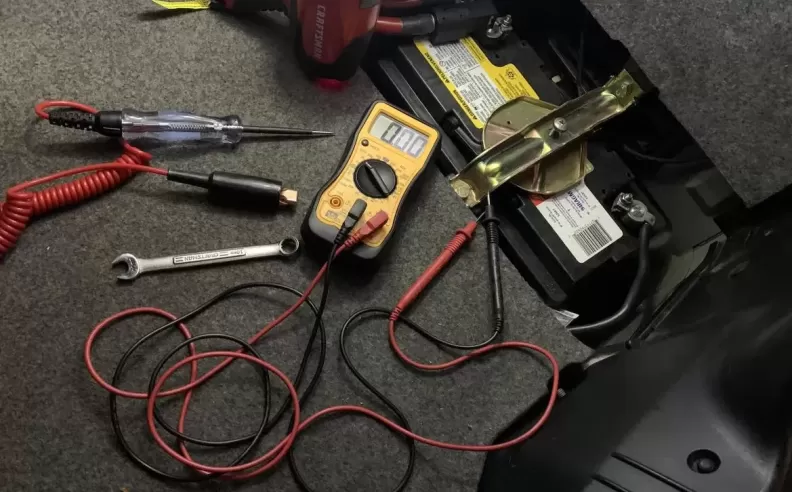

Before delving into troubleshooting, it's essential to gather some information about the problem and assemble the necessary tools. Start by identifying the specific electrical component(s) that are malfunctioning. Common issues include a dead battery, faulty alternator, blown fuses, malfunctioning switches, or damaged wiring. Ensure you have a repair manual or access to reliable online resources for your vehicle's make and model. Additionally, assemble a basic toolkit containing tools like a multimeter, wire connectors, electrical tape, and a test light.
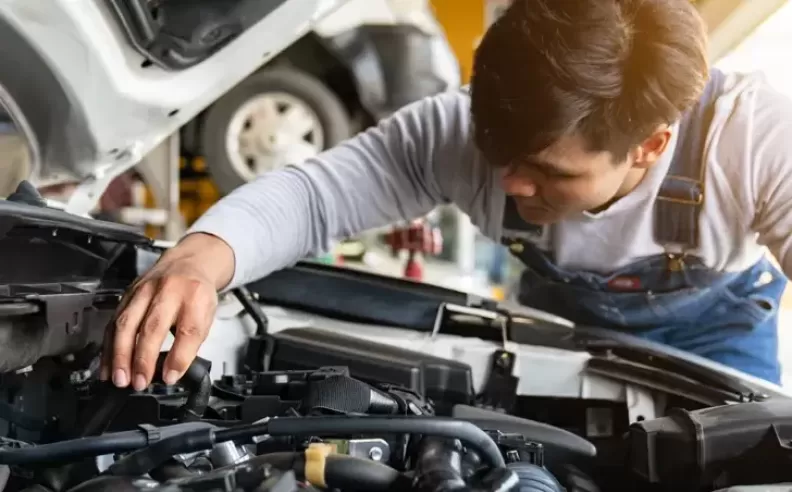

Begin by conducting a thorough visual inspection of the electrical system. Look for loose or corroded connections, damaged wires, and signs of burned or melted components. Pay attention to the battery terminals, fuse box, relays, and ground connections. Also, check for any unusual smells or visible signs of damage. Identifying any obvious issues can help narrow down the problem and save time during diagnosis.
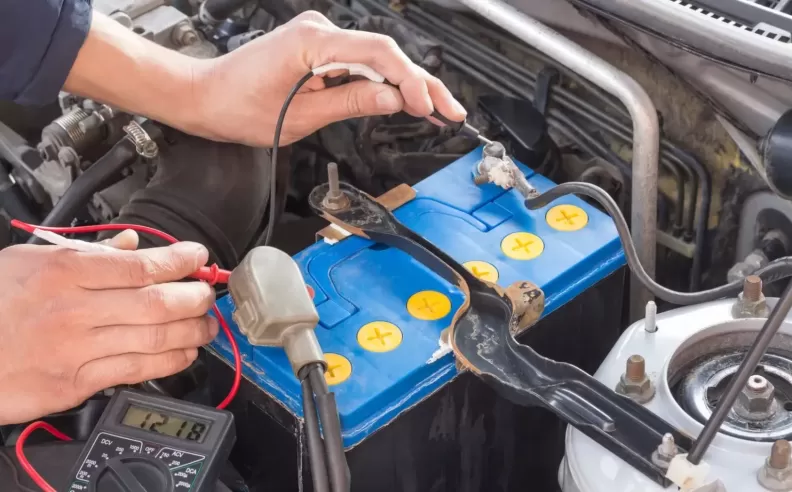

A common culprit for electrical problems is a weak or dead battery. Start by checking the battery voltage using a multimeter. A healthy battery should read around 12.6 volts. If the voltage is significantly lower, try jump-starting the vehicle or charging the battery. If the battery doesn't hold a charge, it may need to be replaced.
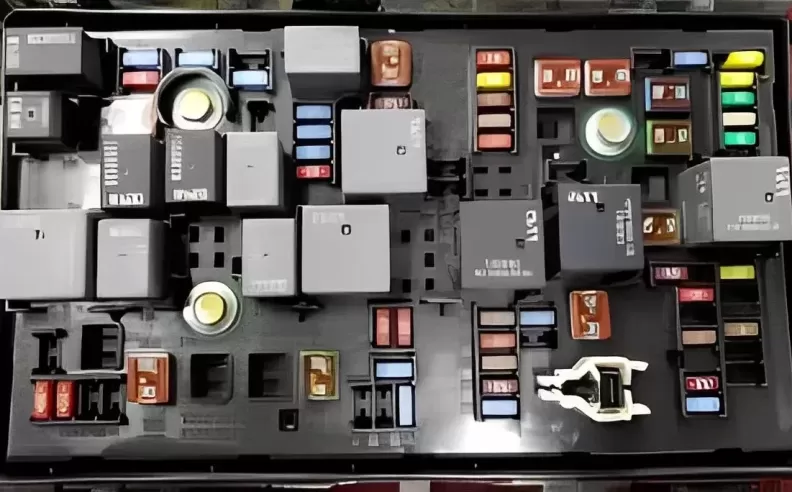

Faulty fuses and relays can cause specific electrical components to stop functioning. Locate the fuse box, typically found under the dashboard or in the engine bay. Consult the owner's manual or fuse box cover for the appropriate fuse and relay diagram. Inspect each fuse visually or use a test light to check for continuity. Replace any blown fuses or faulty relays with new ones of the same rating.
If certain components are not working, such as lights, windows, or the radio, test them individually to identify the problem. Use a multimeter or a test light to check for power supply and continuity at various connection points. If voltage is present but the component doesn't function, the component itself may be faulty and require replacement.
Damaged or loose wiring can disrupt the electrical flow and cause malfunctions. Inspect the wiring harnesses, connectors, and terminals for any signs of damage, frayed wires, or loose connections. Repair or replace damaged wiring as necessary. Ensure all connectors are firmly attached and free of corrosion. Apply electrical tape or heat shrink tubing to secure repaired or exposed wires.
Diagnosing and fixing car electrical problems can be a rewarding experience if approached systematically. By gathering information, conducting visual inspections, testing components, and inspecting wiring, you can often identify and resolve common electrical issues. Remember to exercise caution when working with electrical systems, as mishandling can result in injury or further

Wael is an automotive content writer specializes in creating written content for Motor 283. Producing a wide range of content, including blog posts, articles, product descriptions, reviews, and technical guides related to cars, trucks, motorcycles, and other vehicles, with an unprecedented passion for cars, and motorcycles.

