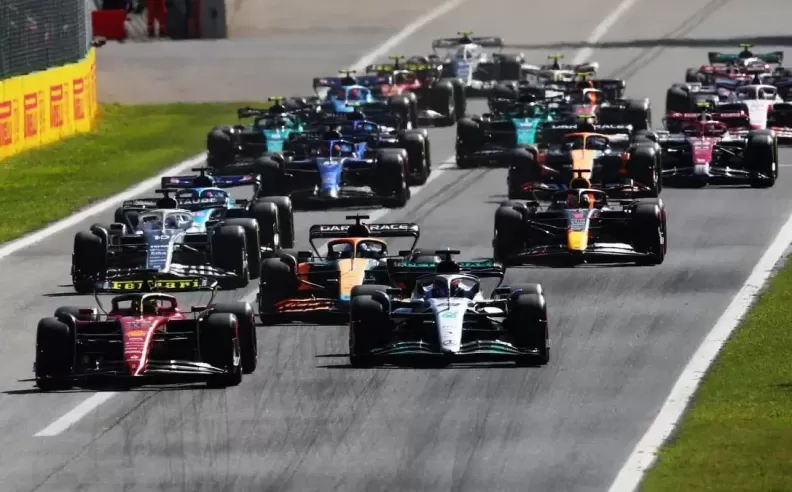
Formula 1 (F1) cars represent the pinnacle of automotive engineering and design. Built for speed, agility, and precision, these machines are a marvel of modern technology and craftsmanship. This article explores the key specifications and design elements that define F1 cars, providing a glimpse into the intricate world of these racing giants.
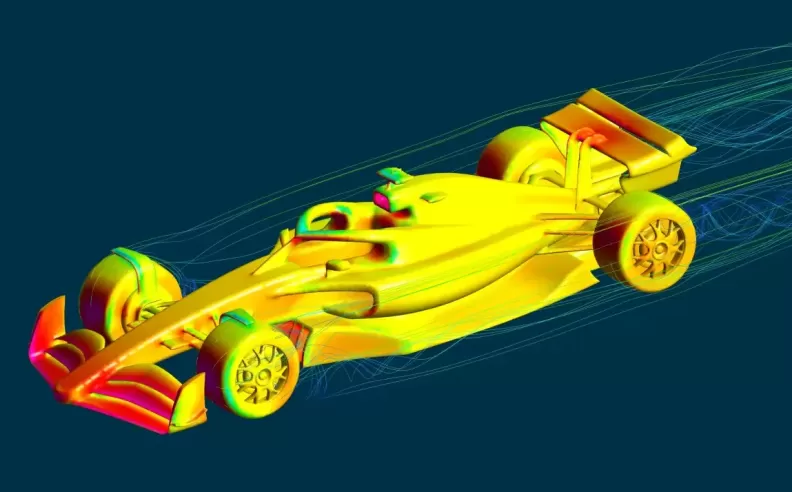

Chassis: The chassis of an F1 car is a monocoque structure, typically made from carbon fiber composites. This construction provides exceptional strength and rigidity while being extremely lightweight. The monocoque not only houses the driver but also serves as the main structural component of the car.
Aerodynamics: Aerodynamics play a crucial role in the design of F1 cars. The goal is to maximize downforce while minimizing drag. The aerodynamic elements include front and rear wings, diffusers, bargeboards, and intricate floor designs. The front wing channels air around the car, optimizing airflow to the rest of the vehicle. The rear wing and diffuser work together to create downforce, pressing the car to the track and increasing cornering speed. Teams invest heavily in wind tunnel testing and computational fluid dynamics (CFD) to refine these components.
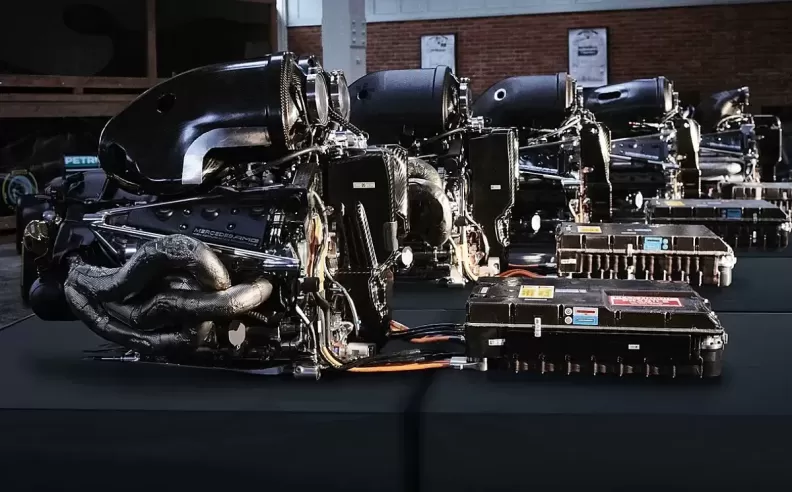
The power unit of a modern F1 car is a complex hybrid system comprising several key components:
Internal Combustion Engine (ICE): A 1.6-liter V6 turbocharged engine serves as the heart of the power unit. It operates at up to 15,000 RPM and produces over 750 horsepower.
Energy Recovery Systems (ERS): The ERS consists of two main components: the Motor Generator Unit-Kinetic (MGU-K) and the Motor Generator Unit-Heat (MGU-H). The MGU-K recovers kinetic energy from braking and converts it into electrical energy, while the MGU-H recovers heat energy from the turbocharger. The energy is stored in a battery and can be deployed to provide an additional power boost.
Turbocharger: The turbocharger compresses the intake air, increasing the engine's efficiency and power output.
Battery and Control Electronics: These components manage the flow of electrical energy within the power unit, optimizing performance and efficiency.
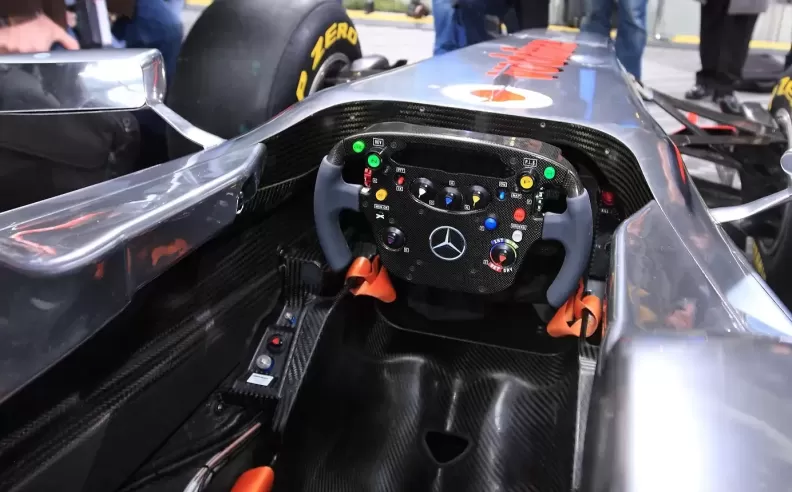

F1 cars use highly sophisticated semi-automatic, sequential gearboxes with eight forward gears and one reverse gear. The gearboxes are made from lightweight materials like titanium and carbon fiber to reduce weight. Gear changes are controlled by paddle shifters mounted on the steering wheel, allowing for rapid and precise shifts. The drivetrain transfers power to the rear wheels, and the differential is finely tuned to manage power delivery, especially during cornering.
Suspension and Tires
The suspension system of an F1 car is designed to maximize mechanical grip and aerodynamic efficiency. It consists of double wishbones, pushrods or pullrods, and torsion bars or coil springs. The suspension geometry is optimized for precise handling and stability.
Pirelli is the exclusive tire supplier for F1, providing different compounds to suit various track conditions and strategies. The tires are critical for performance, as they are the only contact point between the car and the track. Managing tire wear and temperature is a vital aspect of race strategy.
Brakes
F1 cars are equipped with carbon fiber composite brakes, which offer exceptional stopping power and can withstand extreme temperatures. The braking system includes ventilated discs and calipers, with advanced brake-by-wire technology that allows precise control of braking force.
Cockpit and Safety Features
The cockpit of an F1 car is a tightly confined space, designed to protect the driver. Key safety features include:
Halo: A titanium structure that surrounds the driver's head, providing protection from debris and impacts.
Head and Neck Support (HANS) Device: A device that restricts head movement during crashes, reducing the risk of neck injuries.
Fire-Resistant Clothing: Drivers wear specially designed suits, gloves, and boots made from fire-resistant materials.
Telemetry and Data Analysis
Modern F1 cars are equipped with a multitude of sensors that monitor various parameters such as speed, temperature, tire pressure, and more. This data is transmitted to the pit crew in real-time, allowing teams to make strategic decisions and optimize performance during the race.
The design and specifications of Formula 1 cars are a result of continuous innovation and technological advancements. Every component is meticulously engineered to achieve maximum performance, efficiency, and safety. As the sport evolves, so do the cars, pushing the boundaries of what's possible in automotive engineering.

Wael is an automotive content writer specializes in creating written content for Motor 283. Producing a wide range of content, including blog posts, articles, product descriptions, reviews, and technical guides related to cars, trucks, motorcycles, and other vehicles, with an unprecedented passion for cars, and motorcycles.

