As the automotive industry continues to pivot towards greener and more sustainable transportation solutions, hybrid vehicles have emerged as a popular choice among consumers seeking a balance between traditional internal combustion engines and electric propulsion. However, not all hybrids are created equal. Two prominent categories within this segment are full hybrids and mild hybrids, each offering distinct features and benefits. This article explores the key differences between these two types of hybrids, focusing on their operational capabilities and environmental impact.
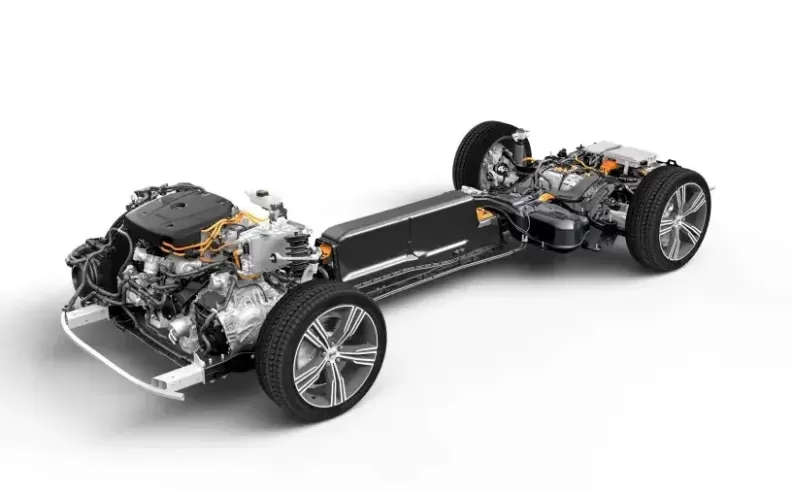

Full hybrid vehicles, often referred to simply as hybrids, are characterized by their ability to operate using either the internal combustion engine, the electric motor, or a combination of both. This flexibility is made possible by a larger and more powerful battery compared to that found in mild hybrids. One of the standout features of full hybrids is their capacity to drive on battery power alone, a capability that significantly enhances fuel efficiency and reduces emissions.
Efficiency and Emissions
According to recent studies, full hybrids can operate in a fuel-efficient, zero-emissions mode up to 62% of the time on average. This is particularly beneficial in urban driving conditions where frequent stops and starts can be managed efficiently by the electric motor, minimizing fuel consumption and tailpipe emissions. The ability to drive on electric power alone not only contributes to lower operational costs but also aligns with global efforts to mitigate environmental pollution and combat climate change.
Practical Benefits
The practical benefits of full hybrids extend beyond environmental considerations. The seamless transition between electric and gasoline power ensures a smooth driving experience, with the electric motor providing immediate torque for quick acceleration. Moreover, the regenerative braking system found in full hybrids captures and stores energy that would otherwise be lost during braking, further enhancing overall efficiency.
In contrast, mild hybrids incorporate a smaller battery and electric motor that do not independently power the vehicle. Instead, the electric motor in a mild hybrid functions primarily as a supportive system to the internal combustion engine. This assistance can take various forms, such as providing an extra boost during acceleration, enabling a smoother start-stop operation, and powering ancillary systems while the engine is off.
Limited Efficiency Gains
The inability of mild hybrids to drive on pure battery power means they deliver fewer benefits compared to full hybrids. While they still offer some improvements in fuel efficiency and emissions reductions, these gains are considerably more modest. Mild hybrids are typically more affordable than their full hybrid counterparts due to their simpler and less expensive battery and motor systems. This makes them an attractive option for consumers looking to reduce fuel consumption without a significant increase in upfront costs.
Role in the Market
Despite their limitations, mild hybrids play an important role in the transition towards more sustainable transportation. They represent a step up from traditional gasoline-only vehicles, providing some environmental benefits and introducing drivers to the advantages of electrification. For many consumers, a mild hybrid can serve as an accessible entry point into the world of hybrid technology.
The choice between a full hybrid and a mild hybrid ultimately depends on the individual needs and priorities of the consumer. Full hybrids, with their ability to operate on electric power alone for a significant portion of the time, offer greater efficiency and environmental benefits. They are ideal for those who prioritize low emissions and fuel savings, particularly in urban settings.
On the other hand, mild hybrids provide a more affordable alternative that still offers some improvements over traditional vehicles. They are well-suited for drivers seeking a balance between cost and efficiency, and who may not require the full capabilities of a hybrid electric vehicle.
As the automotive industry continues to evolve, both full and mild hybrids will play critical roles in reducing reliance on fossil fuels and lowering the environmental impact of personal transportation. By understanding the differences between these technologies, consumers can make informed decisions that align with their driving habits and environmental goals.

Wael is an automotive content writer specializes in creating written content for Motor 283. Producing a wide range of content, including blog posts, articles, product descriptions, reviews, and technical guides related to cars, trucks, motorcycles, and other vehicles, with an unprecedented passion for cars, and motorcycles.

